Troubleshooting
Why is my build not displaying?
This behavior can occur for several reasons that may or may not be visually apparent.
The first step to troubleshooting this issue requires viewing the webhook deliveries for the repository.
This can be accomplished by using one of the following methods:
- UI - Navigate to the
https://vela.example.com/<org>/<repo>/hookspage for the repository - CLI - Run the
vela get hooks --org <org> --repo <repo>command for the repository
After finding the information for the webhook, please use the list below which includes details on how to resolve the issue.
Missing Webhook Signature
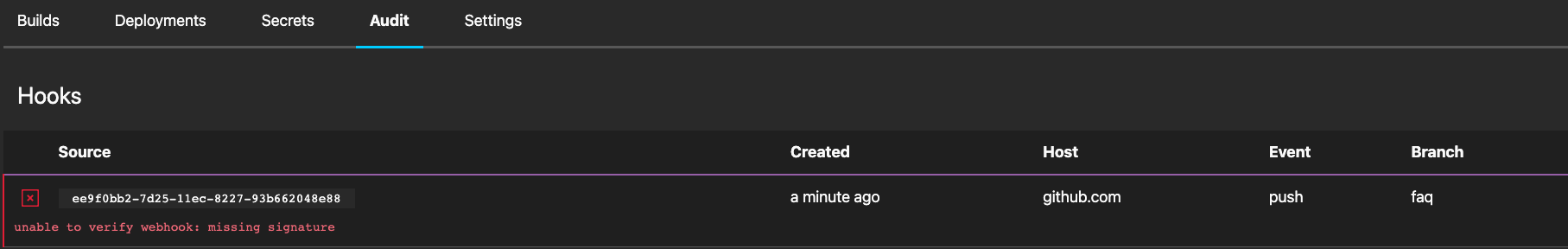
This behavior indicates the signature, used to verify authenticity of the webhook, for the repository has been removed.
To resolve the issue, the repository will need to be repaired which will recreate the webhook with a valid signature.
This can be accomplished by using one of the following methods:
- UI - Click the
Repairbutton on thehttps://vela.example.com/<org>/<repo>/settingspage for the repository - CLI - Run the
vela repair repo --org <org> --repo <repo>command for the repository
An access level of admin is required in order to repair a repository.
Payload Signature Check Failed
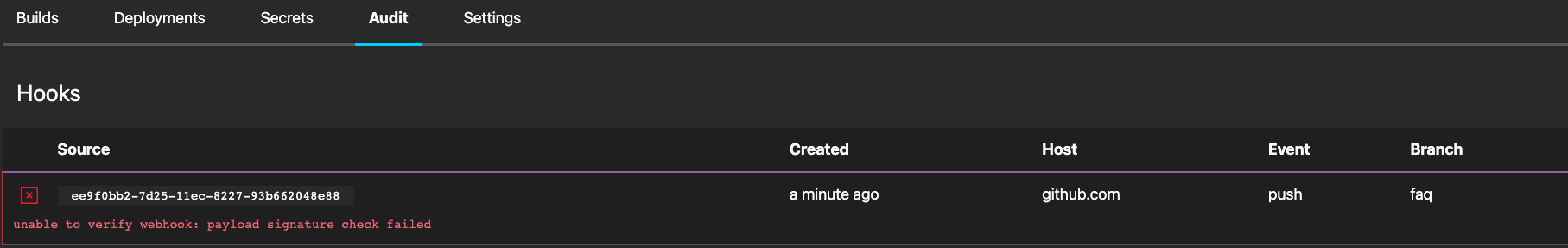
This behavior indicates the signature, used to verify authenticity of the webhook, for the repository has been corrupted.
To resolve the issue, the repository will need to be repaired which will recreate the webhook with a valid signature.
This can be accomplished by using one of the following methods:
- UI - Click the
Repairbutton on thehttps://vela.example.com/<org>/<repo>/settingspage for the repository - CLI - Run the
vela repair repo --org <org> --repo <repo>command for the repository
An access level of admin is required in order to repair a repository.
Repo Exceeded Build Limit
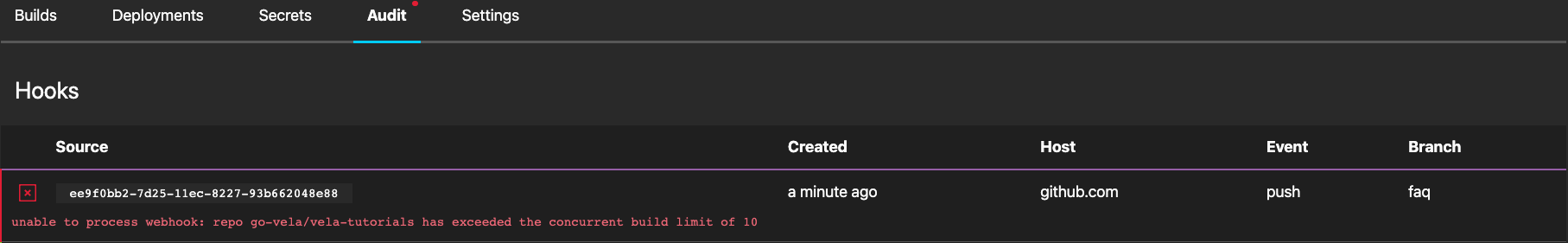
This behavior indicates the number of pending or running builds for the repository exceeded the concurrent build limit.
To resolve the issue, find a build with a pending or running status and cancel it (or wait for it to complete).
This can be accomplished by using one of the following methods:
- UI - Click the
Cancel Buildbutton on thehttps://vela.example.com/<org>/<repo>/<build>page for the repository - CLI - Run the
vela cancel build --org <org> --repo <repo> --build <build>command for the repository
An alternative solution is to increase the build limit for the repository.
This can be accomplished by using one of the following methods:
- UI - Update the
Build Limitfield on thehttps://vela.example.com/<org>/<repo>/settingspage for the repository - CLI - Run the
vela update repo --org <org> --repo <repo> --build.limit <limit>command for the repository
Unable To Unmarshal YAML
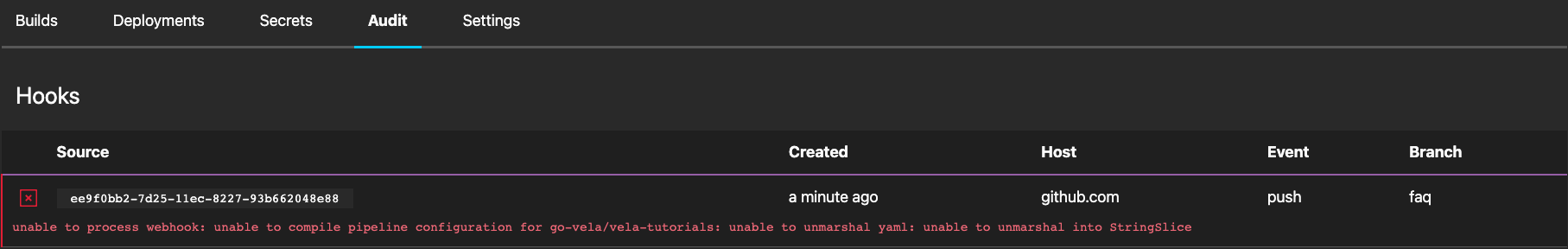
This behavior indicates the pipeline can't be compiled because it includes invalid syntax.
To resolve the issue, identify the incorrect syntax in the pipeline and update it with proper value(s).
This can be accomplished by using the vela validate pipeline CLI command in the directory where the pipeline is located.
Your Account Was Suspended
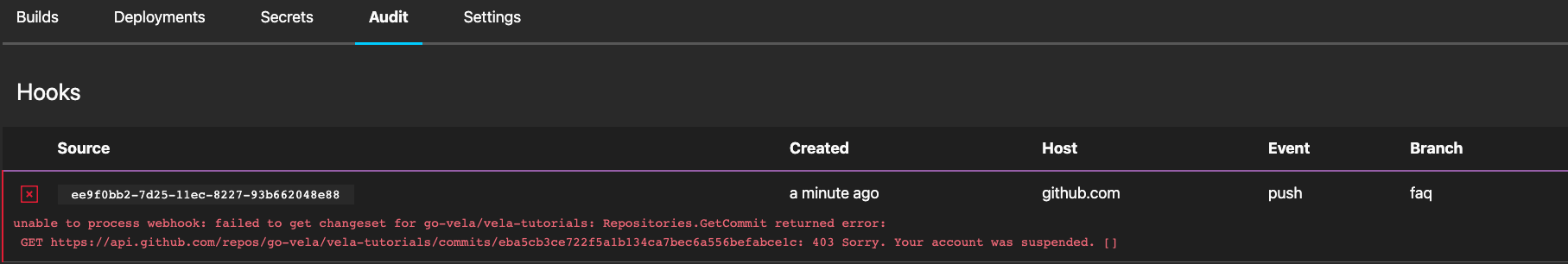
This behavior indicates the user who originally enabled the repository had their account suspended in the SCM.
To resolve the issue, the repository owner will need to be changed to an unsuspended user in the SCM.
This can be accomplished by using one of the following methods:
- UI - Click the
Chownbutton on thehttps://vela.example.com/<org>/<repo>/settingspage for the repository - CLI - Run the
vela chown repo --org <org> --repo <repo>command for the repository
An access level of admin is required in order to change ownership of a repository.
Why is my build not running?
This behavior can occur for several reasons that may or may not be visually apparent.
The first step to troubleshooting this issue requires viewing the build object for the repository.
This can be accomplished by using one of the following methods:
- UI - Navigate to the
https://vela.example.com/<org>/<repo>page for the repository - CLI - Run the
vela get builds --org <org> --repo <repo>command for the repository
After finding the information for the build, please use the list below which includes details on how to resolve the issue.
Build Is Pending
This behavior indicates the number of running builds for the system is greater than the number of workers available.
Unfortunately, the only way to resolve the issue is to wait until a worker becomes available to run your build.
Queue length exceeds configured limit, please wait for the queue to decrease in size before retrying
This error is given in response to a build restart request of a pending build whenever the queue is larger than the configured limit by the platform admins.
This is a measure to prevent queue bloat from builds that are already in the queue.
Context Deadline Exceeded
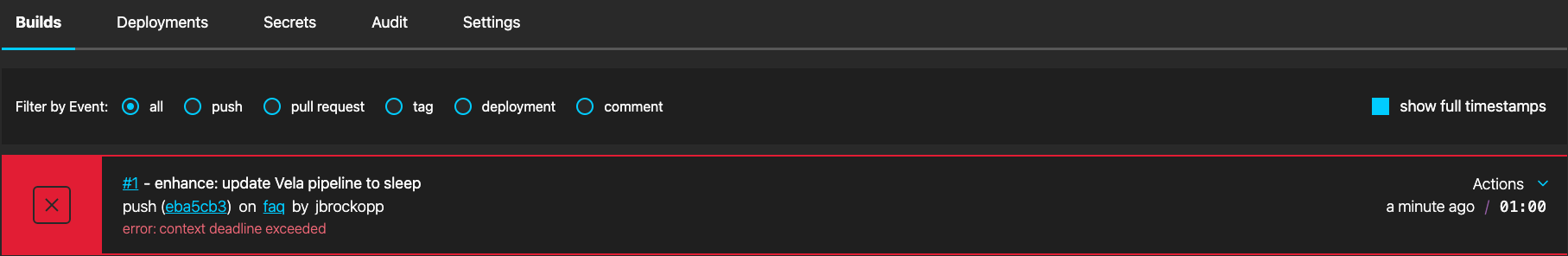
This behavior indicates the amount of time the build was running exceeded the timeout for the repository.
To resolve the issue, optimize the pipeline to improve the performance and decrease the runtime for builds.
This can be accomplished by using one of the following methods:
- Update the pipeline to use rulesets which will limit the number of steps ran in the build
- Update the pipeline to use stages which will enable running steps concurrently
An alternative solution is to increase the build timeout for the repository.
This can be accomplished by using one of the following methods:
- UI - Update the
Build Timeoutfield on thehttps://vela.example.com/<org>/<repo>/settingspage for the repository - CLI - Run the
vela update repo --org <org> --repo <repo> --timeout <timeout>command for the repository
Invalid Reference Format
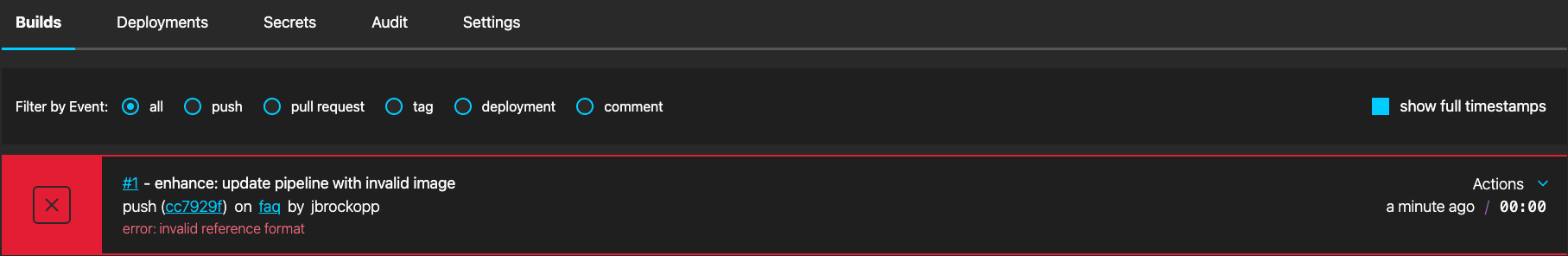
This behavior indicates the image key provided for a step in the pipeline is invalid.
To resolve the issue, identify the step with the incorrect image and update it with a proper value.
This can be accomplished by using the docker pull CLI command with the value for the image as the first argument.
Invalid Secret Path

This behavior indicates the key property provided for a secret in the pipeline is invalid.
To resolve the issue, explicitly define the secret depending on the type as outlined in the secret usage docs with all of the expected fields.
If you are using a secret that only defines name as the property and are receiving this error, you will need add the missing properties as this way of referencing a secret was deprecated in an older version of Vela.
For example:
secrets:
- name: foo
and even
secrets:
- name: foo
key: foo
engine: native
type: repo
would need to be changed to:
secrets:
- name: foo
+ key: <org>/<repo>/foo
+ engine: native
+ type: repo
Make sure to replace <org> and <repo> for the key property with the appropriate values from your source code provider.
If you're using GitHub and using the secret for a pipeline at https://github.com/octocat/hello, your org would be octocat and repo would be hello.
Repo is not trusted
This behavior indicates the vela_executor_enforce_trusted_repos flag has been set by the Vela platform administrators, which allows only certain repositories to run privileged images.
To resolve the issue, identify the step attempting to run a privileged image and consider a workaround. Otherwise, work with your Vela platform administrators to add your repository to the allowlist.
v0.26 YAML Migration
With the release of v0.26, Vela transitioned away from buildkite/yaml to the official go-yaml/yaml for parsing pipelines and templates.
As a result, there are a few common parsing issues that have been compiled together here:
Issue 1: unable to unmarshal into StringSliceMap
This error indicates that Vela is failing to unmarshal the environment key in one or many steps in your pipeline.
This can be caused in two different ways.
Cause 1: inline Go "clobbering" pre-defined YAML environment key
environment:
STATE: California
CITY: San Francisco
NEIGHBORHOOD: Embarcadero
{{ if <something> }}
NEIGHBORHOOD: Mission
{{ end }}
Because NEIGHBORHOOD was already declared outside the inline Go logic, it will cause issues with the YAML parser. Instead of re-assigning the environment key, users should declare the key solely within the inline Go:
Solution
environment:
STATE: California
CITY: San Francisco
{{ if <something> }}
NEIGHBORHOOD: Mission
{{ else }}
NEIGHBORHOOD: Embarcadero
{{ end }}
Now the NEIGHBORHOOD key is not being re-assigned. It is being declared via Go logic.
Cause 2: multiple << keys within the environment map (will be addressed as a warning in v0.26.2)
base_env: &base_env
CLUSTER: my_cluster
REGION: us-west
release_env: &release_env
ENV: prod
steps:
- name: release step
image: my_image
environment:
REPO: ${VELA_REPO_FULL_NAME}
<<: *base_env
<<: *release_env
commands:
- ./do_release.sh
The above environment merge will throw an error because the << key is repeated, which violates the unique key constraint in standard YAML maps. To remediate, simply declare all your alias YAML nodes in a sequence.
Solution
base_env: &base_env
CLUSTER: my_cluster
REGION: us-west
release_env: &release_env
ENV: prod
steps:
- name: release step
image: my_image
environment:
REPO: ${VELA_REPO_FULL_NAME}
<<:
- *base_env
- *release_env
commands:
- ./do_release.sh
Issue 2: missing parameters or environment pairs when using YAML anchors
This issue occurs when users have declared an anchor which contains some base set of parameters or environment pairs and attempts to add them to step configurations which have their own parameters or environment pairs. Below is an example.
plugin_base: &plugin_base
image: my-neat-plugin:v1.2.3
pull: always
secrets: [ plugin_token ]
parameters:
log_level: debug
repo: ${VELA_REPO_FULL_NAME}
steps:
- name: plugin-west
<<: *plugin_base
parameters:
region: central
data_center: west
- name: plugin-east
<<: *plugin_base
parameters:
region: central
data_center: east
Due to the fact that parameters is a declared key in the plugin_base anchor and in the steps plugin-west + plugin-east, the YAML parser will only accept the parameters declared in the steps. This is the YAML standard, which unfortunately was not followed by our previous parser.
To solve this issue, users should plan on merging parameters and environment maps with separate map anchors that avoid collisions.
Solution
plugin_base: &plugin_base
image: my-neat-plugin:v1.2.3
pull: always
secrets: [ plugin_token ]
plugin_base_params: &plugin_base_params
log_level: debug
repo: ${VELA_REPO_FULL_NAME}
steps:
- name: plugin-west
<<: *plugin_base
parameters:
<<: *plugin_base_params
region: central
data_center: west
- name: plugin-east
<<: *plugin_base
parameters:
<<: *plugin_base_params
region: central
data_center: east
Now when Vela compiles the pipeline, the parameters blocks for each step will include the log_level and repo pairs from the base anchor.